
Functionalized Gold Nanoparticles: Get More from Your Gold
Uses of Functionalized Gold Nanoparticles
What benefits do functional nanoparticles have over other gold nanoparticles?
The true promise of gold nanoparticles is controlling their unique properties at the molecular. Functionalized gold nanoparticles offer an ability to selectively target delivery to various cell types and tissues. This opens possibilities for improved bioimaging, drug delivery, biosensing, rapid diagnostic tests, and various other therapeutic and diagnostic applications.
Without targeted delivery, the nano-scale of AuNPs facilitates entry into nonselective cells. However, by conjugating biomolecules and ligands to the surface of gold nanoparticles researchers are able to utilize targeted strategies. Unlike other gold nanoparticles, functionalized gold offers a simple and straightforward means to accomplish robust and stable conjugation to achieve targeted gold nanoparticles. Further, because of the generic "click chemistry" used to conjugate these nanoparticles, conjugation possibilities are endless and can be easily tailored to specific research applications.
For more information about uses and benefits of Functionalized Gold Nanoparticles see the Nanomaterials Review: Functionalized Gold Nanoparticles and Their Biomedical Applications
Available Functionalized Gold Nanoparticles
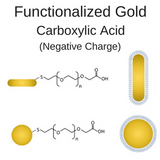
Carboxylic Acid Functionalized Gold Nanoparticles
Negatively charged carboxylic acid gold nanoparticles facilitate covalent conjugation to positively charged primary amines found at the N-terminus of polypeptide chains and in the side group of the amino acid lysene.
Click here for more information on Carboxyl Functionalized Gold Nanoparticles.
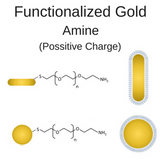
Amine Functionalized Gold Nanoparticles
Positively charged amine gold nanoparticles facilitate covalent conjugation via acylation with activated carboxylic acids, reductive amination with aldehydes, reaction with isothiocyanates to produce thioureas, and alkylation with epoxides.
Click here for more information on Amine Functionalized Gold Nanoparticles.
PEGylated Gold Nanoparticles
Neutrally charged mPEG Gold Nanoparticles provide the highest stability among functional gold nanoparticles. The inert surface increases in vivo circulation and reduces immunogenicity. However, conjugation to ligands or biomolecules is more difficult than other functional groups.
Click here for more information on mPEGylated Gold Nanoparticles.

Coming Soon
Functionalized Gold Nanoparticles soon to be available
- Malemide Functionalized Gold Nanoparticles
- Silica-Coated Gold Nanoparticles with Functional Surfaces
