Ask an Expert: What is CTAB and why is it toxic? Why is it used in gold nanorod synthesis?
CTAB, [(C16H33)N(CH3)3Br], also known as cetyltrimethylammonium bromide; hexadecyltrimethylammonium bromide; and cetrimonium bromide is a cationic surfactant.
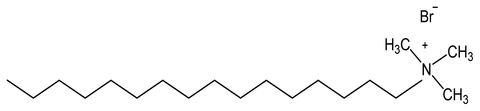
Figure 1: Chemical structure of CTAB
The basic synthesis of Au nanorods is accomplished by the controlled reduction of a gold salt in the presence of CTAB and small amounts of silver. CTAB is utilized to direct the growth of Au nanorods and stabilize them after synthesis. CTAB is a bromine-containing surfactant that forms stable, elongated micelles in water. The silver in solution forms a complex with the bromine of CTAB, which preferentially adsorbs to the gold. This bond inhibits growth in the axial direction, allowing preferential lengthening of the gold crystal. Rod thickness and length can be controlled by adjusting the concentration of CTAB, controlling the pH, or introducing other surfactants. CTAB-stabilized gold nanorods are stable if stored in the correct conditions.
The toxicity of CTAB occurs due to two active mechanisms:
1) CTAB is a positively charged surfactant that is highly attracted to negatively charged cell membranes. Its interaction with the phospholipid bilayer destabilizes the cell membrane, and results in reduced cell membrane integrity or 'holes' leading to cell death,
2) The catalytic action of one of CTAB’s dissociation products, the CTA+ cation, which might cause the quenching of the enzyme ATPsynthase and thus lead to energy deprivation and death of the cell. Our studies indicate that this second mechanism, which depends on the concentration of CTA+, is the most lethal.
Though gold nanorods are synthesized using CTAB to ensure monodispersity, we can make our nanorods biocompatible by replacing the CTAB after synthesis with molecules, such as polyethylene glycol (PEG), to eliminate CTAB-associated cytotoxicity and improve in vivo circulation times. Customers who would like to conjugate gold nanorods with antibodies and other moieties can purchase CTAB-stabilized gold nanorods and displace the coating with thiolated antibodies.
Ask an Expert:
Have a question for our scientists about working with gold nanoparticles? Submit your question using this quick form.
Related links:
Plasmonic properties of gold nanorods
Ask an expert: What is the difference between citrate, CTAB, PEG & Silica coatings?


